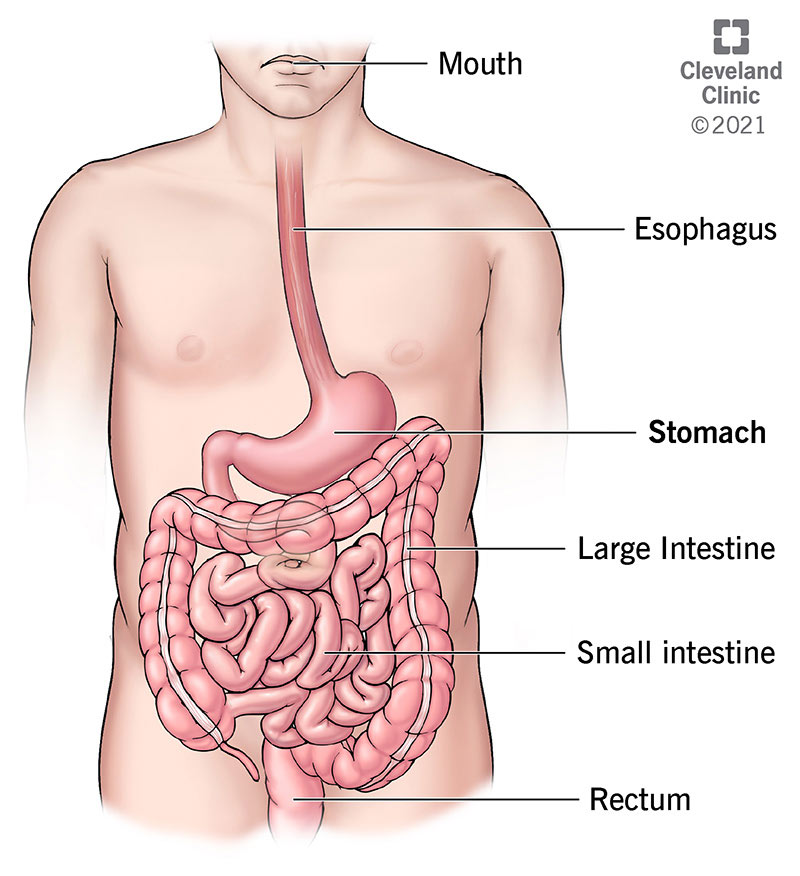
Describe the Structure of the Stomach and Explain Its Function
Il make a little list of the adaptations of the stomach to its function. Some textbooks describe it as being the first part of the small intestine.
Stomach Anatomy Function Diagram Parts Of Structure
The stomach muscles contract periodically churning food to enhance digestion.
. The stomach located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen is a J-shaped organ composed predominantly of involuntary smooth muscle. Structure of the duodenum. In animals whose stomachs contain digestive glands some of.
Science Assignment Help Stomach Describe the structure of the stomach. Start your trial now. First week only 499.
The stomach is J-shaped and it can expand to temporarily store food. The enzyme pepsin is responsible for protein breakdown. It secretes HCl and pepsin apart from other things including mucus.
Cells in the lining of your stomach secrete a strong acid and powerful enzymes that are responsible for the breakdown process. Glands in the fundus that secrete gastric juice. Mouth is the opening through which intake of food occurs.
Describe the structure of the stomach and explain its function Answer. Describe the functions of the components of gastric juice. The stomach has an acid wish helps in digestions and also kills germs it also has enzymes which aid in.
We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts. The core function of the human stomach is as an aid to digestion. See answer 1 Best Answer.
Describe stomach structure and indicate changes in the basic alimentary canal structure that aid its digestive function. Function of esophagus. Palate -It forms the roof of the oral cavity.
How does It compare to that of the fetal pig. Has goblet cells that secrete alkaline mucus which traps rich HC03- fluid underneath. The reservoir capacity of the stomach allows it to increase its volume.
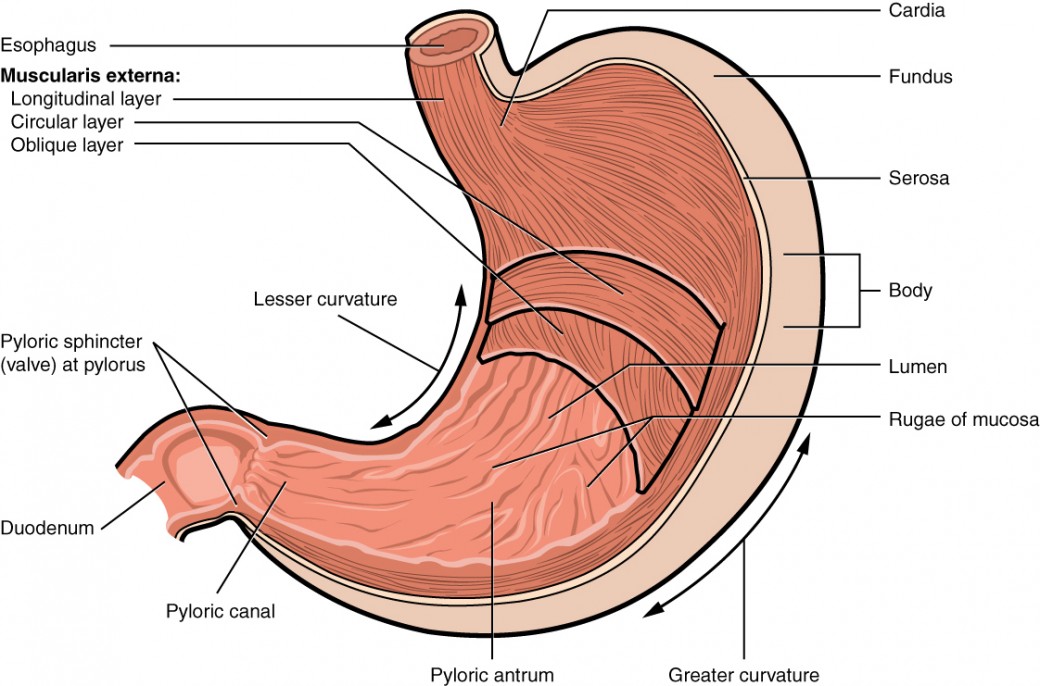
The funnel-shaped pylorus connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pyloric sphincter is a muscular valve that opens to allow. The narrower end is called the pyloric canal which connects to the duodenum.
Function of the stomach. Biology Assignment Help Structure of the stomach Describe the structure of the stomach. The churning action of the stomach muscles physically breaks down the food.
This article will outline the structure and function of the duodenum. Weve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments. Relate the structure of the stomach to its functions.
A bolus of food enters the stomach through the lower oesophageal sphincter which rapidly closes to prevent regurgitation of gastric secretions see part 1. The alimentary canal gastrointestinal tract GI is a continuous coiled hollow muscular tube that winds through the ventral body and is open Cal both ends. The stomach secretes acid and enzymes that digest food.
The stomach releases acids and enzymes for the chemical breakdown of food. It produces enzymes substances that create chemical reactions and acids digestive juices. The stomach is an organ of the digestive system specialized in the accumulation and digestion of food.
Function of pharynx. The wider end of the funnel the pyloric antrum connects to the body of the stomach. Solution for Describe the structure of the stomach.
The duodenum the jejunum and the ileum. Textbook solution for Human Biology 15th Edition Sylvia Mader Chapter 93 Problem 1LO. The oral cavity has three parts palate tongue and teeth.
-The stomach is folded up to begin with then as food. The stomach is a hollow organ or container that holds food while it is being mixed with stomach enzymes. The small intestine is made up of thee sections.
Ridges of muscle tissue called rugae line the stomach. Its anatomy is quite complex. The stomach serves as a temporary receptacle for storage and mechanical distribution of food before it is passed into the intestine.
If we were to locate it on our bodies it can be found on our left side just below the ribs. Because of this the frequency of eating is reduced. How is it modified to carry out its functions.
The stomach is a J-shaped organ that digests food. They keep food and secretions from going down the windpipe and prevents acid and stomach contents from traveling backwards from. How does it compare to that of the fetal pig.
These enzymes continue the process of breaking down food into a usable form. This mix of enzymes and digestive juices breaks down food so it can pass to your small intestine. It is a continuation of the esophagus and receives our churned food from it.
The duodenum is located in your gastrointestinal tract just past the stomach. Below the fundus is the body the main part of the stomach. Anatomy and functions.
Innervation is provided via the vagus nerves and the celiac plexus. Describe the most common cause of stomach ulcers and. Also has 5 additional cells that secretes gastric juice mucus and gastrin into the gastric pits.
The stomach is a muscular organ that is found in our upper abdomen. Swallowing food has the epiglottis to prevent food from going down trachea Structure of esophagus. Partial digestion of the food takes place here.
How is it modified to carry out its functions. Stomach saclike expansion of the digestive system between the esophagus and the small intestine. In this article we will discuss about the function of stomach.
Finally explain the causes of heartburn and why the stomach does not digest itself. On its proximal near end the small intestinebeginning with the duodenumconnects to the stomach. The four key components of gastric digestive function are its function as a reservoir acid secretion enzyme secretion and its role in gastrointestinal motility.
In simple terms the stomach is a kind of digestive sac. The esophagus is a muscular tube connecting the throat pharynx with the stomach. It acts as a temporary storage organ.
The parts of the digestive system include mouth oral cavity teeth esophagus pharynx stomach small intestine large intestine and anus. On its distal far end the ileumthe last segment of the small intestineconnects to the large intestine colon. The core function of the human stomach is as an aid to digestion.
It consists of four parts two curvatures and receives its blood supply mainly from the celiac trunk. It is located in the anterior portion of the abdominal cavity in most vertebrates.
The Stomach Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Gastrointestinal Tract 2 The Structure And Function Of The Stomach Nursing Times
Stomach Structure Function Digestive System Anatomy And Physiology
Comments
Post a Comment